PB-PENTAdb
Database of pentapeptides from protein structures
A database of pentapeptides is derived and weekly updated from PDB and SCOP 1.75a culled at 100% sequence identity (astral100 dataset) but also at lower sequence identities filtering. A sliding window of 5 residues is used to extract the coordinates of every pentapeptide contained in all polypeptide chains featured in PDB or in SCOP. The dihedral phi and psi angles are then calculated and mapped to a trained Kohonen map of 16 cells each representing a local structure prototype (the protein blocks) named a, b, c, … , n, o, p according to the methodology developed by de Brevern et al (2000). Each pentapeptide hence extracted is assigned to the protein block (PB) with which it has the lowest rmsda value (angular root mean square deviation). Information about the amino acid sequence, the PB, the dihedral angles, the secondary structure (assignment by DSSP), solvent accessibility (calculated as per NACCESS) and backbone B-factors are stored in PB-PENTAdb database.
The whole process for building the database is illustrated below: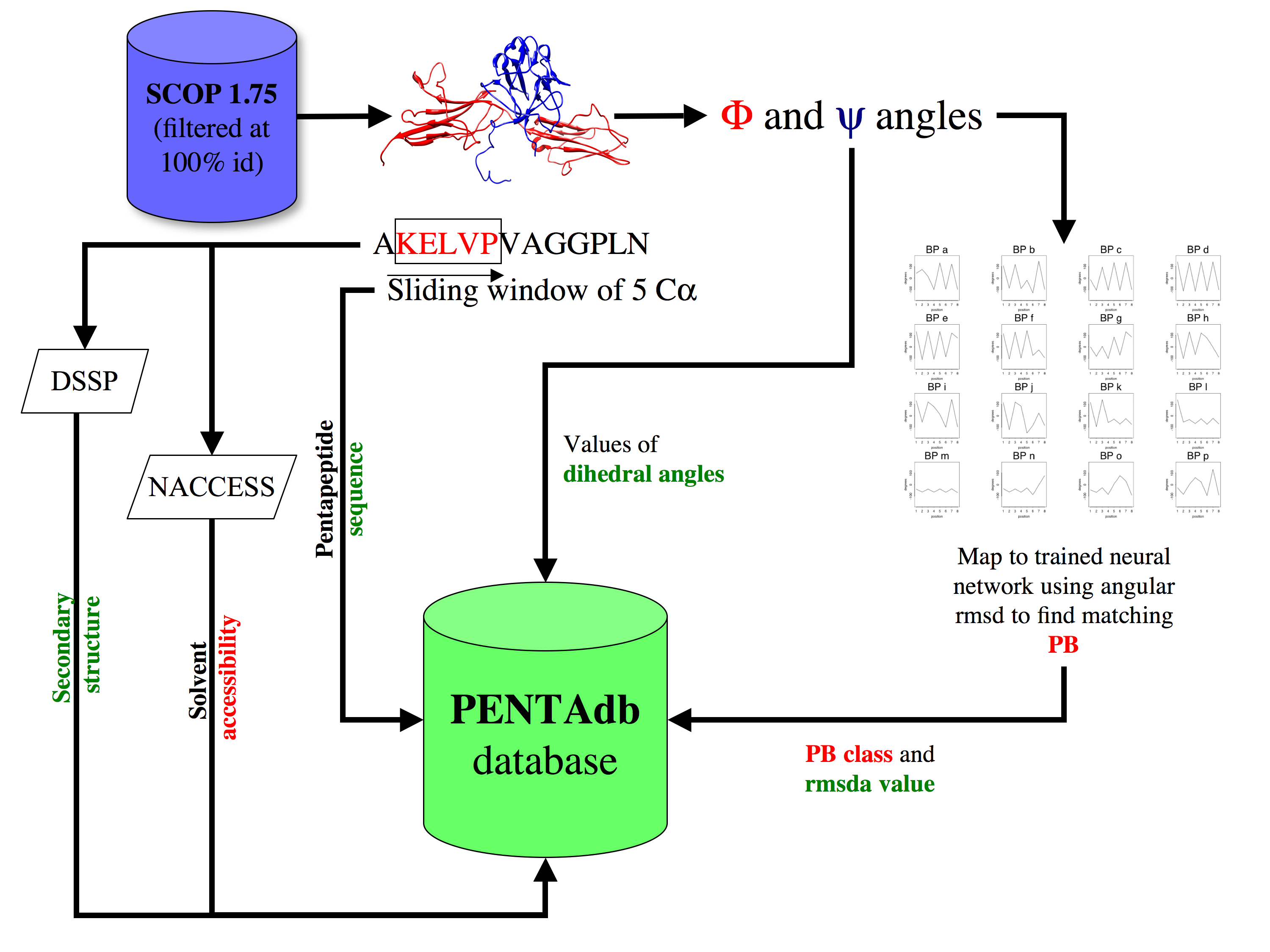 |
Query formThe program takes as input a pentapeptide amino acid sequence in the input text box below. |
As output, a table is provided with
- the pentapeptide sequence
- the PB
- the SCOP id of the domain where this pentapeptide is extracted
- the position of the first residue of the pentapeptide in the domain
- a series of psi and phi values
- the secondary structure assignment (from DSSP)
- a series of 5 values corresponding to the “all atoms” relative solvent accessibility for all 5 residues
- a series of backbone B factors